How to curb bleeding and bruising in cancer patients
Sep 28, 2022
Share
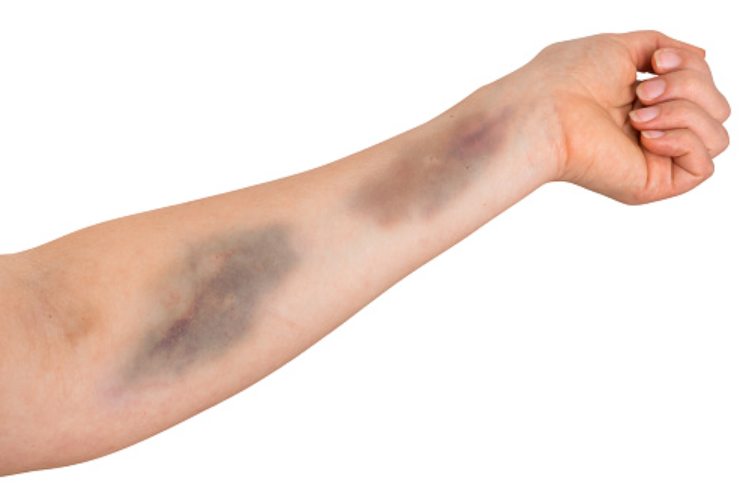
Bleeding and bruising in cancer patients is mainly associated with the failure of various factors controlling blood clotting. Clotting is mainly affected by; weak blood vessels, low platelet count, poor platelet function, and low vitamin K in the body. Low platelet count and poor platelet function (thrombocytopenia) are the main reasons for bleeding and bruising by cancer patients.
The whole issue of bleeding in cancer patients could be quite mystifying. However, don’t worry because we have the condition covered under this blog. You can also find more information presented by Laura in our “bruising treatment video” on YouTube.
Reasons for bleeding and bruising in cancer patients
Patients may experience bleeding and bruising due to; cancer itself, cancer treatment, medicines like blood thinners and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and surgeries for tumor removal. Other causes could be angiogenesis (which involves the growth of new blood vessels in cancer tumors) and local tumor invasions.
Causes and Symptoms of bleeding and bruising in cancer patients
Below is a brief explanation of each of these bleeding bruise causes in cancer patients:
Thrombocytopenia
This results from a low platelet count in the patient’s blood. Malfunctioning of the platelets is also a form of the thrombocytopenia problem.
One of the thrombocytopenia causes is chemotherapy which involves damaging tissues inside the bone… but the damage doesn’t last forever.
Antibodies responsible for the production of proteins that kill viruses and bacteria may at times destroy healthy platelets.
Cancer that spreads to the bone or the spleen may affect platelet levels. That’s because cancer in bones means that the bone marrow won’t produce new platelet cells. Also, cancer inhabiting the spleen occupies space where extra platelets should be stored.
Note: Platelets are tiny blood cells produced in the bone marrow. They stick together during an injury to form a plug or a clot which should stop bleeding.
Here are some symptoms of thrombocytopenia:
- Prolonged bleeding when injured.
- Running nose and gum bleeding.
- Blood in urine, vomit, or stool.
- Heavy menstrual cycles.
- More bruises than usual.
- Muscle and joint pains.
Other Factors
Also known as coagulopathy factors, these may lead to poor blood clotting in cancer patients’ body systems. One of these includes liver problems when the liver doesn’t produce enough clotting factors. Therefore, this causes bleeding from the liver or other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Liver cancer is also another major cause of bleeding which you can notice by having blood in the urine.
Lack of vitamin K (VK) in cancer patients is also a common factor common. Medical procedures like chemotherapy cause nausea and lowers your appetite. Appetite loss could lead to malnourishment and low intake of enough VK-rich foods will lead to easy bleeding.
Treatment and Control
Here is how you can take care of cancer bleeding and bruising:
Thrombocytopenia – Treatment of thrombocytopenia could be challenging in case the patient has other underlying conditions. However, radiation therapy, reduced chemotherapy, and platelet transfusion are some of the recommended solutions. Additionally, medications like oprelvekin can help accelerate platelet production during itp treatment.
Vitamin K – You can easily prevent Vitamin K deficiency by taking a variety of foods, especially vegetables.
Conclusion
Our medical team at OncoPower can guide you through the management process and precisely walk you through every step. You can also get more insights from videos on our Oncopower app. Our associates specializing in cancer-related issues will advice you on how to handle the problem.
Trusted by cancer patients around the world.
Joan-Smith
Virginia, United States
ChuckHastings
Florida, United States
DebraPearl
Pennsylvania, United States
Jennweeks
Iowa , United States
PatrickDW
Western Cape, South Africa
Jamie-Alexander
Floroda United States
CJ
Liz
Florida, United States
NYCynthia
New York, United States
Ferdi
California, United States